10.27.17
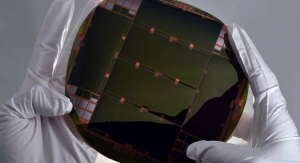
Scientists at the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) reported significant advances in the thermoelectric performance of organic semiconductors based on carbon nanotube thin films that could be integrated into fabrics to convert waste heat into electricity or serve as a small power source.
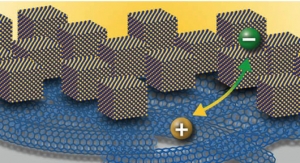
The research demonstrates significant potential for semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as the primary material for efficient thermoelectric generators, rather than being used as a component in a “composite” thermoelectric material containing, for example, carbon nanotubes and a polymer. The discovery is outlined in the new Energy & Environmental Science paper, Large n- and p-type thermoelectric power factors from doped semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotube thin films.
“There are some inherent advantages to doing things this way,” said Jeffrey Blackburn, a senior scientist in NREL’s Chemical and Materials Science and Technology center and co-lead author of the paper with Andrew Ferguson. These advantages include the promise of solution-processed semiconductors that are lightweight and flexible and inexpensive to manufacture. Other NREL authors are Bradley MacLeod, Rachelle Ihly, Zbyslaw Owczarczyk, and Katherine Hurst. The NREL authors also teamed with collaborators from the University of Denver and partners at International Thermodyne, Inc., based in Charlotte, N.C.
Ferguson, also a senior scientist in the Chemical and Materials Science and Technology center, said the introduction of SWCNT into fabrics could serve an important function for “wearable” personal electronics. By capturing body heat and converting it into electricity, the semiconductor could power portable electronics or sensors embedded in clothing.
Blackburn and Ferguson published two papers last year on SWCNTs, and the new research builds on their earlier work. The first paper, in Nature Energy, showed the potential that SWCNTs have for thermoelectric applications, but the films prepared in this study retained a large amount of insulating polymer. The second paper, in ACS Energy Letters, demonstrated that removing this “sorting” polymer from an exemplary SWNCT thin film improved thermoelectric properties.
“We could actually fabricate the device from a single material,” Ferguson said. “In traditional thermoelectric materials you have to take one piece that’s p-type and one piece that’s n-type and then assemble those into a device.”
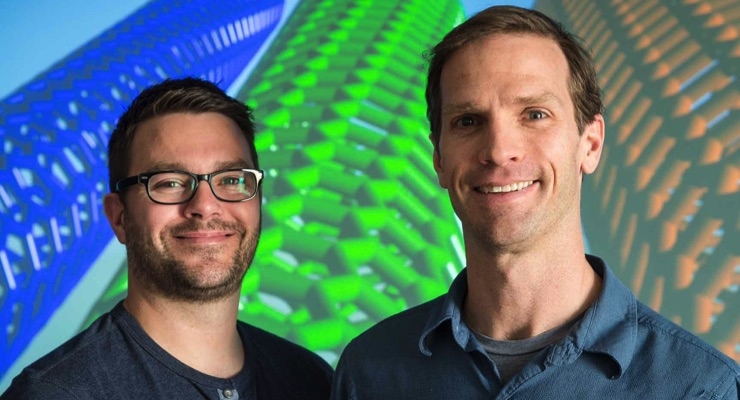

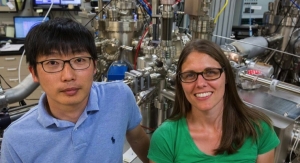
NREL scientists Andrew Ferguson, left, and Jeffrey Blackburn stand in front of a screen displaying single-walled carbon nanotubes. (Photo by Dennis Schroeder/NREL)
The research demonstrates significant potential for semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as the primary material for efficient thermoelectric generators, rather than being used as a component in a “composite” thermoelectric material containing, for example, carbon nanotubes and a polymer. The discovery is outlined in the new Energy & Environmental Science paper, Large n- and p-type thermoelectric power factors from doped semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotube thin films.
“There are some inherent advantages to doing things this way,” said Jeffrey Blackburn, a senior scientist in NREL’s Chemical and Materials Science and Technology center and co-lead author of the paper with Andrew Ferguson. These advantages include the promise of solution-processed semiconductors that are lightweight and flexible and inexpensive to manufacture. Other NREL authors are Bradley MacLeod, Rachelle Ihly, Zbyslaw Owczarczyk, and Katherine Hurst. The NREL authors also teamed with collaborators from the University of Denver and partners at International Thermodyne, Inc., based in Charlotte, N.C.
Ferguson, also a senior scientist in the Chemical and Materials Science and Technology center, said the introduction of SWCNT into fabrics could serve an important function for “wearable” personal electronics. By capturing body heat and converting it into electricity, the semiconductor could power portable electronics or sensors embedded in clothing.
Blackburn and Ferguson published two papers last year on SWCNTs, and the new research builds on their earlier work. The first paper, in Nature Energy, showed the potential that SWCNTs have for thermoelectric applications, but the films prepared in this study retained a large amount of insulating polymer. The second paper, in ACS Energy Letters, demonstrated that removing this “sorting” polymer from an exemplary SWNCT thin film improved thermoelectric properties.
“We could actually fabricate the device from a single material,” Ferguson said. “In traditional thermoelectric materials you have to take one piece that’s p-type and one piece that’s n-type and then assemble those into a device.”

NREL scientists Andrew Ferguson, left, and Jeffrey Blackburn stand in front of a screen displaying single-walled carbon nanotubes. (Photo by Dennis Schroeder/NREL)